

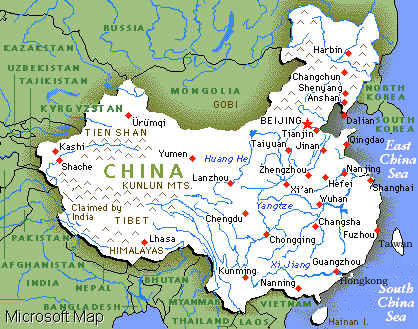
 The People¨s Republic of China is situated in the east of Asia,
adjoining Korea in the east, and Vietnam, Laos, Burma in the south, bordering on India,
Bhutan, Sikkim, Nepal, Pakistan and Afghanistan in the southwest and west, the former
Soviet Union in the northwest and northeast, and Mongolia in the north, and close to
Japan, Philippines, Malaysia, Indonesia, Brunei and other countries and regions. With an
area of about 9.6 million square kilometers.
The People¨s Republic of China is situated in the east of Asia,
adjoining Korea in the east, and Vietnam, Laos, Burma in the south, bordering on India,
Bhutan, Sikkim, Nepal, Pakistan and Afghanistan in the southwest and west, the former
Soviet Union in the northwest and northeast, and Mongolia in the north, and close to
Japan, Philippines, Malaysia, Indonesia, Brunei and other countries and regions. With an
area of about 9.6 million square kilometers.
High in the west, and low in the east, China has a varied topography, among which mountainous regions cover 33% of area, plateau 26%, hills 10%, basin 19%, plain 12%. Most of rivers such as the Heilongjiang River, the Haihe River, the Huanghe River, the Huajhe River, the Changjiang River and the Zhujiang River, etc. flow into the Pacific Ocean.
Climate
With a vast territory, China stretches across the temperate zone and torrid zone. Most of the areas are located in the north temperate zone and subtropical zone and controlled by the monsoon climate of east Asia. Because of varied topography and great difference of the elevation and the distances between land and sea, China has varied climates. For example, there is no summer in the north part of Heilongjiang Province. On the country, in Hainan island, there is no winter. In the Huaihe River valley the four seasons of the year could be identified easily. It¨s like spring all the year round in the south part of the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau. The Qinghai-Tibet Plateau is covered with snow all the year round. In the inland of the northwest China it is hot in summer and cold in winter, with a great difference in temperature. From September or October every year to March or April next year, China is controlled by the dry monsoon and it is cold and dry in the whole country, with winter in China is about 5-18 C lower than that in the other areas with same latitude. From April to September every year, influenced by the humid and warm air current blew from the sea, it is mostly very hot and rainy in the broad areas in the southeast of the mountain chain constructed by the Greater Xing¨an Mountains, the Yinshan Mountains, the Helan Mountains, the Nayar Har Mountains and the Gangdise mountains. In July the temperature range between Guangzhuo and Harbin is only 60C. There are great differences in annual rainfall among different areas of southeast China, and gradually get some decreases in the inland areas, with that in northwest under 50mm. The wet monsoon prevails from July to August and brings much rainfall.
(Source: Country Report of China, May 1995)
|
|
Copyright: Institute of Crop Germplasm Resources,CAAS, All Rights Reserved |